The following guide will create a shortcut that opens Command Prompt as Administrator, equivalent to right click on Command Prompt and select “Run as Administrator to gain full administrator access tokens and credentials. Useful if you don’t want to turn off UAC but always need to run commands in elevated Command Prompt. You can double-click or tap on the Administrator’s Command Prompt shortcut directly to open an elevated Command Prompt, just like you would for any other apps. The shortcut can be placed on anywhere, including Desktop, Start Menu, Taskbar, Start Screen, any folders and etc.
- Right-click on Windows desktop.
- On the right click context menu, choose New, and then select Shortcut.
- When the “Create Shortcut” dialog box appears, type in Cmd into the text box, and then click Next.
- Type a name for the shortcut (typically Command Prompt or Command Processor) on the next screen, and then press Finish.
- Right-click on the new shortcut created.
- On the right click pop-up contextual menu, select Properties.
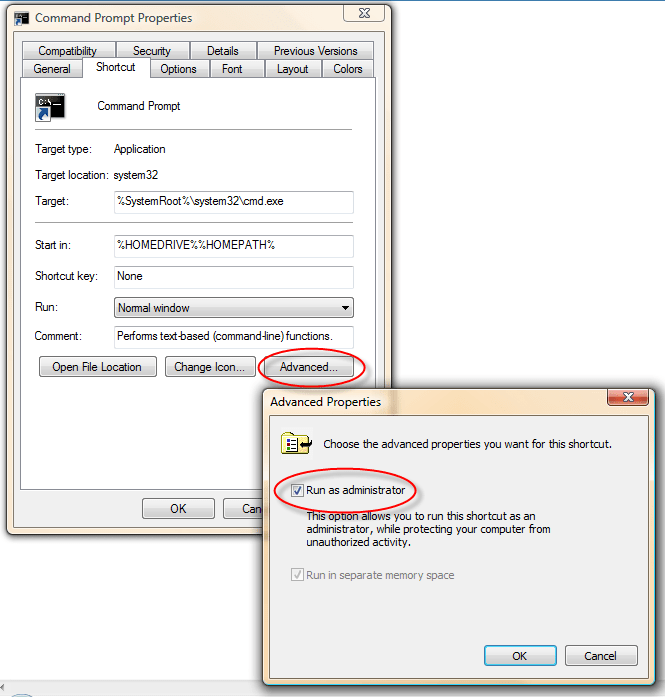
- Click on the Shortcut tab.
- Click on the Advanced button to open Advanced Properties dialog box.
- Tick or check (select) the Run as administrator option so that the command prompt will be launched with administrator privileges by default, and then click OK.
- Click OK again to finish.
Alternatively, you can pin a Cmd.exe command to Start Menu or Taskbar and configured it to run as administrator:
- Click on Start button.
- Type Cmd into the Search box.
- You will see search result with a list consisting of just one entry, that is the shortcut to the Windows Command Processor, Command Prompt or Cmd.
- Right-click the Command Prompt or Cmd in the search listing.
- On the pop-up context menu, choose Pin to Start Menu or Pin to Start. If you prefer to pin to Taskbar, choose Pin to Taskbar.
- Click on Start button again.
- Right-click the Command Prompt shortcut just added to the Start menu and choose Properties.
- Click the Advanced button to open Advanced Properties dialog box.
- Click (tick) to select the Run as administrator checkbox so that elevated command prompt is run as administrator by default, and then click OK.
- Click OK to save the changes.
From Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10 or later, you can just open the Power Users menu, and select Command Prompt (Admin) to open an elevated Command Prompt with full access tokens.